Narrow special interests are politically powerful if
- members of the special interests are less motivated to go to the polls.
- they are not organized.
- they are favored only by the minority political party.
- the benefits are concentrated while the costs are spread out through society.
Attempts to reduce excess capacity through mergers violate (may violate) U.S. antitrust laws if
- there is no increase in concentration.
- The Justice Department is ideologically sympathetic.
- the takeover attempts are hostile.
- they are likely to result in higher prices.
Global carbon emission transferable quotas based on historical emission levels would
- penalize countries with high current per capita emission.
- force poor countries to buy quotas from rich countries if they want to grow their output.
- force rich countries to buy quotas from poor countries.
- Both A and C.
Offshoring and outsourcing of complete rungs of the intra-firm career ladder is conducive to
- upward job mobility within firms for workers joining at the very bottom if the middle section of the ladder is missing.
- higher labor costs when third-party suppliers are more efficient.
- dead-end jobs in specialized firms with short career ladders doing the outsourced bottom-rung jobs.
- shorter formal education for internal upward mobility for workers joining at the bottom of the top half if the bottom half is missing.
Load pricing is
- possible only for pricing electricity.
- easy to implement at little detection cost.
- a way to price according to average cost rather than marginal cost.
- a way to force consumers to internalize the external congestion cost at peak hours.
The internet has enabled new two-sided markets because
- it has created new surplus capacity on the supply side.
- the information cost for transactions is drastically reduced.
- it has created new demand for the supply-side surplus capacity.
- people with surplus capacity are more willing to share for free.
Major networked airlines are susceptible to price competition from niche startups because
- startups can offer more connections than the majors.
- startups can challenge the majors on thinly traveled routes.
- the major airlines have high fixed network costs.
- startups can sustain loss much longer than the major airlines.
If the Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) is larger than the actual
exchange rate between Norway and the US, that means the ______ price of
Big Mac in Norway is _________ in the US.
- dollar; higher than the dollar price
- dollar; lower than the dollar price
- krona; lower than the kroner price
- Both A and C.
In a coordination game with multiple stable equilibriums,
- people prefer to have one single standard than no standard.
- people do not know ahead of time which standard is the best standard over time.
- the winning standard is always the collectively superior standard.
- All of the above.
- Both A and B.
Transparent pricers would lose sales to loss-leader pricers if all buyers
- are sophisticated.
- are myopic.
- pay attention to high hidden fees.
- Both A and C.
When labor is scarce relative to capital, which of the following should be maximized?
- Output per unit of labor and capital.
- Output per unit of land.
- Output per unit of capital.
- Output per unit of labor.
High transaction cost to transfer or to enforce property rights
- might impede the transfer of property rights to higher-value uses.
- makes the original assignment of property rights unimportant for their eventual assignment.
- promotes efficient use of resources.
- helps to reduce externality.
Price support sets the price
- Higher than the market-clearing price.
- Lower than the market-clearing price.
- At the same level as the market-clearing price.
- Below the cost of production.
Auctioning quotas to the highest bidders ensures that the economic rent
- goes mostly to the winning bidders.
- is close to being maximized.
- goes mostly to the quota issuing agency.
- Both B and C.
Unregulated spending on political campaigns is
- An ever-escalating arms race that does not have an equilibrium solution.
- A fixed-level Nash equilibrium.
- A collectively superior solution.
- Both B and C.
In a closed economy, actual savings will increase only if
- the output pie shrinks.
- consumption is reduced.
- investment is reduced.
- what is saved is recycled back to investment.
Which of the following is correct in the short run when some input is fixed?
- When total variable cost increases at a decreasing rate, marginal cost will decrease.
- Diminishing returns sets in when total variable cost increases.
- When total variable cost increases, marginal cost will increase.
- Diminishing returns refers to diminishing marginal cost.
A Nash equilibrium is
- A solution from which one has no incentive to escape given others' choice.
- Always a collective superior solution.
- Always an inferior solution.
- A trap from which one is powerless to escape.
Certain (as opposed to uncertain) information on the incidence of risk could
- encourage adverse selection of membership in the insurance risk pool.
- encourage moral hazard on the part of the insured.
- discourage the low-risk group from buying insurance.
- Both A and C.
- discourage the high-risk group from buying insurance.
The preferences of consumers for superstars and hit mass products have contributed to
- the concentration of income at the top.
- too few people chasing the star dreams.
- a more even distribution of income.
- the average income being lower than the median income.
Restriction on technology transfer to low cost countries would
- make it unnecessary to move up the technology ladder for mature products.
- increase the cost of importable components used by domestic end users.
- preserve jobs for mature industries with low profit margin.
- provide incentives for domestic companies to upgrade its technology.
A country with persistent trade surpluses can reduce them
- by a combination of currency appreciation and domestic price rises.
- only by raising its domestic prices and wages.
- only by currency appreciation.
- by sterilizing the inflow of foreign currencies.
A perfect price discriminator
- worries about massive defection of its customers.
- does not have to worry about customer price arbitrage.
- has many competitors.
- receives marginal revenue equal to its price.
Surge pricing
- enriches Uber only without clearing the market.
- limits quantity demanded only.
- expands quantity supplied only.
- expands quantity supplied and limits quantity demanded.
In the absence of adequate information, insurers are likely to
- welcome moral hazard.
- practice statistical discrimination.
- encourage adverse selection.
- charge every insured the same premiums.
Issuing rebate coupons rather than an across-the-board price discount is a cheaper way to promote a product because
- coupons cost nothing to print and distribute.
- those who do not redeem their coupons do not get the price discount.
- most consumers would redeem their coupons.
- more buyers are likely to redeem coupons than taking advantage of a straight price discount.
China has a greater dependence on exports for its GDP growth than Germany because
- its export/GDP ratio is higher than Germany's.
- the value-added contents of China's exports is higher than Germany's.
- China's exports compete on lower-value-added contents than Germany's.
- higher value-added products are less subject to competition.
- Both C and D.
People are bad at evaluating odds because they
- are easily persuaded by full information.
- usually think that all outcomes are equally probable.
- rely on what readily comes to their minds.
- are overwhelmed by too much organized information.
Low wage shares in global GDP are not sustainable because
- wages are the only source of demand for output.
- profit cannot be spent on consumption.
- profit cannot be spent on what is not consumed.
- there is not sufficient demand to absorb the total output.
Flat-rate (all you can use) pricing is profitable for sellers if
- it involves additional cost for buyers to use as much as they think they would.
- the right of use can be transferred to friends.
- It includes usually expensive items.
- there is no minimum pre-paid subscription period.
Government incentives are costly because
- the incentives fail to produce short-term effects.
- it is difficult to channel the incentives only to incremental activities.
- only unintended recipients benefit from them.
- only intended recipients benefit from them.
Loss-leader pricing can be profitable for sellers if
- customers can freely combine complementary loss-leader items from different vendors.
- customers can stock up loss-leader items for later use.
- other non-price-leader items are competitively priced and the loss-leader does not generate much higher customer traffic.
- myopic customers become captive to complementary services which are premium-priced.
Free parking generates maximum consumer surplus when
- one driver's demand reduces the chance of other drivers getting the same spaces.
- the number of parking spaces is fewer than the number of spaces demanded at zero price.
- more people want parking spaces than are available.
- the number of spaces demanded at zero price is equal to or fewer than the number of parking spaces available.
In the short run, average variable cost excludes ______, while average total cost includes ________.
- fixed cost; fixed cost
- fixed cost; only variable cost
- variable cost; only variable cost
- Both A and B.
Why might some people choose to pay more (buying tickets) to fly than to take a bus for long-distance travel?
- Traveling by bus actually costs more for those whose time cost is higher.
- Traveling by bus costs less only for those whose time costs is lower.
- Both A and B.
- Long-distance buses do not have restrooms.
Flexible work schedules to match customer traffic
- turns fixed labor cost into variable labor cost.
- can lead to lower labor productivity from the same number of workers.
- turns variable labor cost into fixed labor cost.
- require little adjustment of the personal lives of workers.
Houses near the airport are usually cheaper because
- residents must sue the airport to collect damages.
- the lower housing cost is a compensation for the unwelcome airport noise.
- airport noise is an uncompensated external cost.
- Both A and B.
Uber poses competition to taxi companies because
- Uber rides are less expensive than taxi rides.
- taxi fares are not tightly regulated.
- the number of Uber cars in service can be increased without getting a taxi medallion.
- Uber drivers earns less than taxi drivers.
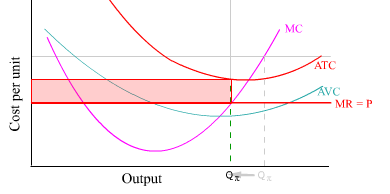
Comparing MR and MC alone do not tell us whether the price-taking firm is making or losing money in the short run because
- MC does not take into account variable cost.
- MR = MC maximizes efficiency not profit.
- Only the P and ATC can tell us whether the firm is making or losing money where MR = MC.
- All of the above.
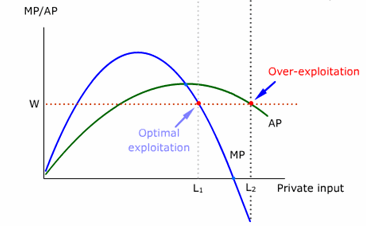
A commons resource tends to be over-exploited because
- users would use it as long as MP (marginal benefit) is not zero.
- users would use it as long as (AP) average benefit is positive.
- users would use it as long as AP (average benefit) is at least equal to W (marginal cost).
- users would use it as long as the MP (marginal benefit) is at least equal to W (marginal cost).
When demand is inelastic,
- a 10% decrease in price would lead to 10% increase in quantity demanded.
- a given percentage change in price would lead to an equal percentage change in quantity demanded.
- total revenue would go down as price falls.
- All of the above.
A dominant preference for boys is likely to be exacerbated by
- Single-child policy.
- Sex-selective technology.
- The presence of old-age social security.
- All of the above.
- Both A and B.
Commercial TV network broadcast can be free because
- there is no viewer congestion and viewers can be charged indirectly when they buy the advertised products.
- there is no way to exclude non-paying viewers of any TV programs.
- viewers simply would not pay for TV programs.
- it costs nothing to broadcast TV programs.
When should new property rights be auctioned off instead of given out for free?
- When the government intends to preserve the value of existing capital investment.
- When the new rights are granted in exchange for de facto rights.
- When the government wants to reward special interests.
- When the government wants to capture the economic rent from the new rights.
Circular flow will stay the same size if
- planned leakages exceed planned injections.
- actual leakages are equal to actual injections.
- planned injections are equal to planned leakages.
- planned injections exceed planned leakages.
______ buyers prefer ______ while _______ buyers prefer _________.
- Novice; wide choices; well-informed; limited choices
- Well-informed; wide choices; novice; limited choices
- Well-informed; limited choices; novice; wide choices
- Well-informed; wide choices; novice; wide choices
Which of the following payment methods would encourage the
highest attendance of an event according to the behavioral theory of
sunk cost?
- Pre-paid tickets sold before the event with a partial rebate for actual attendance.
- Sell tickets at the door.
- Pre-paid tickets sold before the event.
- Phone reservation of tickets to be paid at the door.
Suppose a gas station got some gas delivery at the pre-Katrina
price of $2.00 per gallon. After Katrina, the gas delivery price went
up to $2.50. The opportunity cost of its old gas after Katrina
- averaged between $2.00 and $2.50 per gallon.
- stayed at $2.00 per gallon.
- had gone up to $2.50 per gallon.
- None of the above.
Price discrimination
- generates more consumer surplus when it is successful.
- generates less profit when it is successful.
- is difficult because goods purchased at lower prices could be resold at higher prices.
- denies consumers with lower reservation prices.

It makes sense for the price taker to stay in business in the short run even though P < ATC because
- there is no fixed cost in the short run.
- the firm only needs to pay for variable costs.
- price may be high enough to cover all the variable costs and part of the fixed cost.
- Both A and B.
The U.S. chicken business has been profitable by
- integrating the process from conception to consumption.
- paying low wages to match low labor productivity.
- turning a branded product into a commodity.
- horizontally integrating the production process.
What might prolong the dominance of networked or standards-based products?
- increasing average total cost for large output.
- user lock-in due to high switching cost.
- users are independent of each other.
- government protection.
Inflow of hot money fuels inflation in high-interest developing economies because
- it forces the local interest rate down and encourages more speculative borrowing.
- it forces the local interest rate down and discourages speculative borrowing.
- it raises the local interest rate and encourages more speculative borrowing.
- it decreases the supply of local money.
In an economic recession, higher consumption is good because
- higher rate of saving would further erode aggregate demand for goods and services.
- it leads to higher saving.
- higher spending on ANY investment would simply increase the productive capacity which is already under-utilized.
- it reverses the spending multiplier effect.
Leveraging and deleveraging ____________ the business cycles by _________ optimism and pessimism.
- dampen; restraining
- amplify; restraining
- dampen; reinforcing
- amplify; reinforcing
Why are property rights necessary for internalizing negative externalities?
- Externalities exist only when all property rights are clearly defined and enforced.
- Only those who have no property rights are entitled to demand internalization of negative externalities.
- Only those who have property rights are supposed to suffer from negative externalities.
- Without property rights, we don't know who is supposed to pay whom to resolve externalities.
One way to discourage cheaper knock-off products is to
- postpone the introduction of cheaper versions until the market for the more expensive version is saturated.
- introduce cheaper versions to compete with cheaper knock-off products when the competing products appear.
- sell different versions of the same products at different price points simultaneously.
- charge very high prices to maximize short-term profit.
If we buy more at every price,
- the demand curve must have shifted to the right.
- demand must have increased.
- the law of demand must be wrong.
- Both A and B.
The family wage-gap between women without children and women with children might have
- discouraged highly educated women from having any (or as many) children as they otherwise would.
- led to a higher concentration of children born to more-educated women with higher opportunity costs.
- encouraged career women to have children at a younger age.
- led to a higher concentration of children born to less-educated women with higher opportunity costs.
An external cost occurs
- when one party's action adversely impacts other parties and the property rights of the receptors have not been defined.
- when one party intentionally causes harm to other parties even though the victims have been adequately compensated.
- when one party's action adversely impacts other parties and the victims have been adequately compensated.
- when one party fails to include the cost of harm to other parties even though he has the right to cause harm.
A cover charge in a busy entertainment business on top of the ordered items
- is a form of single pricing.
- encourages customers who have more time than money.
- discourages customers who have more money than time.
- forces those customers who spend a long time nursing a cheap item to pay for part of the fixed cost.
Mass piracy is most likely to occur when
- The marginal cost (MC) of reproduction is high but the R and D cost (i.e., fixed cost) of coming up with the original is low.
- Every item is unique and expensive to produce.
- The price charged is much higher than the marginal cost (MC) of piracy.
- All of the above.
- Both A and C.
In the case of external cost, assigning property rights where none existed before amounts to
- turning a commons resource into a private resource.
- internalizing an external benefit.
- a private resource into a commons resource.
- externalizing an internality.
The tragedy of the commons occurs because
- Cattle tend to eat too much.
- the social marginal benefit is less than the private marginal cost.
- Everybody's business is somebody's business.
- the property rights of some resources have not been defined and enforced.
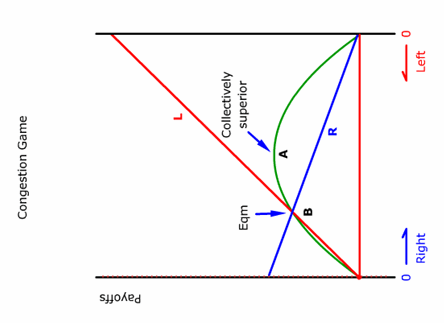
When the payoff curves in a congestion game are not symmetrical, uncoordinated
individual activities often lead to a solution which
- is collectively optimal.
- may not be collectively optimal.
- may not be a Nash equilibrium.
- Both A and B.
Buyers of legal software must cover at least the __________ in
the long run, while pirates pay for only the _______ of copying the
software.
- average total cost; average variable cost
- average total cost; marginal cost
- average variable cost; marginal cost
- average fixed cost; marginal cost
China's trade surplus with the US is a
- mirror image of US's excessive domestic saving.
- mirror image of China's excessive domestic consumption.
- mirror image of China's excessive domestic saving
- mirror image of US's excessive domestic consumption.
- Both C and D.
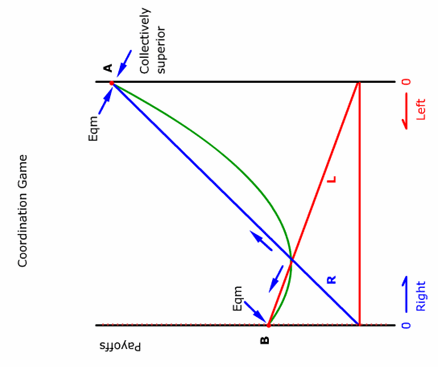
In a coordination game with multiple stable equilibriums,
- the chosen solution may not be collectively superior to the unchosen one.
- the chosen solution is a Nash equilibrium.
- it is easy to migrate from one equilibrium to another.
- Both A and B.
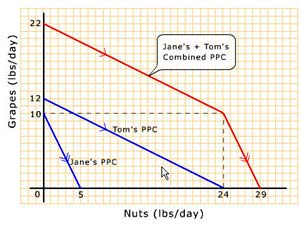
In terms of the relationship between comparative advantage and
opportunity cost in a two-workers and two-goods economy with two
differently-sloping straight-lined downward-sloping PPCs (or PPFs),
which of the following is true?
- When Tom's opportunity cost of nuts in terms of grapes forgone is lower than Jane's, Tom has a comparative advantage in producing grapes.
- When Tom's opportunity cost of nuts in terms of grapes forgone is lower than Jane's, Jane has a comparative advantage in producing nuts.
- When Tom's opportunity cost of nuts in terms of grapes forgone is lower than Jane's, Tom has a comparative advantage in producing nuts.
- When Jane's opportunity cost of grapes in terms of nuts forgone is lower than Tom's, Tom has a comparative advantage in producing grapes.
Single pricing is preferred to perfect price discrimination by consumers
- with reservation prices higher than the single prices.
- with reservation prices lower than the single prices.
- because the consumer surplus received by those with reservation prices higher than the single prices always exceeds the consumer loss suffered by those consumers who cannot afford the single prices.
- because single pricing generates more consumer surplus for all consumers.
A company enjoys longer market dominance by introducing
- A rush product hoping to sell enough to justify later and better versions.
- An acceptable product that satisfies some unfilled needs with refinements in later versions.
- A perfect product with all conceivable functionalities from the get go.
- A product that competes solely on the basis of lower prices.
Price-fixing
- is not against the U.S. antitrust law.
- is a survival strategy for mature industries producing homogeneous products with large scale-economy and excess capacity.
- is a form of capacity reduction.
- increases consumer surplus.
Which of the following will encourage the highest subscription renewal rate?
- Renewal reminder 6 months before expiration date.
- Bonus prize for early renewal.
- Automatic subscription renewal plan with credit card data on file.
- Renewal reminder 2 months before expiration date.
Which of the following is correct in a prisoner's dilemma game?
- The higher the cost of detecting defectors, the larger will be the percentage of defectors.
- The higher the cost of detecting defectors, the smaller will be the percentage of defectors.
- The percentage of defectors is not affected by the cost of detecting defectors.
- The lower the cost of detecting defectors, the larger will be the percentage of defectors.
If firms are not allowed to make economic profit, consumers will benefit
- In the short run.
- In the short and long run.
- At the expense of innovative products
- All of the above.
- Both A and C.
If labor costs, tax rates and regulatory burdens are different across countries,
- the least mobile resources will reap most of the benefits of advantage arbitrage.
- resources will flow from low-cost and low-burden areas to high-cost and high-burden areas.
- resources will flow from high-cost and high-burden areas to low-cost and low-burden areas.
- mobile resources will be stuck with high cost and high burden.
The present-bias effect leads to procrastination
- When choice involves immediate rewards and distant cost.
- When choice involves immediate costs and distant rewards.
- When current abstinence will not lead to greater future rewards.
- When immediate rewards exceeds distant costs.
Monetary policy (maintained by the _________) becomes _______
policy (maintained by the legislature) when _______ money ends up
facilitating government borrowing to fund budget _________.
- central bank; fiscal; tight; deficits
- legislature; fiscal; tight; deficits
- legislature; fiscal; cheap; surpluses
- central bank; fiscal; cheap; deficits
Free parking when parking spaces are scarce would
- favor the time poorer but money richer.
- generate lower total benefit than paid parking that fully allocates the spaces.
- generate higher total benefit than paid parking because those who can't afford parking fee may still be able to get a parking space.
- lead to more efficient time allocation among drivers.
The initial allocation of property rights does not hinder later transfers of the rights
- regardless of how complete and secure the rights are.
- regardless of the transaction cost.
- if the transaction cost is zero and the rights are complete and secure.
- as long as the rights are complete and secure.
White flight in residential neighborhood is
- a dominant strategy.
- individually smart.
- collectively dumb.
- All of the above.
- Only A and C.
Most environmental problems exist because the environment is
- subject to consumption non-rivalry but difficult to restrict access.
- subject to consumption rivalry but easy to restrict access.
- subject to consumption rivalry but difficult to restrict access.
- subject to consumption non-rivalry but easy to restrict access.
Mixed bundling can increase total net revenue when
- demands are positively correlated.
- demands are negatively correlated and marginal costs are positive.
- demands are concentrated in the middle range of individual prices.
- Both B and C.
Generic drugs are cheaper because
- generic drugs are subject to price control
- generic-drug makers are non-profits.
- they are not as potent as the brand-name drugs.
- their makers do not have to pay for the R & D costs to develop the drugs.
The whole concept of price gouging is based on the mis-guided idea that
- people with more urgent needs should be allowed to express them by their willingness to pay more.
- people with more urgent needs should not be allowed to express them by their willingness to pay more.
- merchandise pricing should be based on opportunity cost rather than historical cost.
- All of the above.
Which of the following is correct?
- When the fixed input has very limited capacity, diminishing returns will quickly set in.
- When average total cost is rising due to diminishing returns, marginal cost is below the average total cost.
- When average total cost is falling due to increasing returns, marginal cost is above average total cost.
- When the fixed input has very large capacity, diminishing returns will quickly set in.
When average income is increasing while median income is decreasing, income growth must have concentrated at the
- middle income groups.
- top income groups.
- bottom income groups.
- Top and bottom income groups.
An open standard benefits consumers because
- open standard would encourage the entry of closed proprietary standards.
- the licensing fee for using the open standard is no higher than using the closed standard.
- sellers using the open standard are forced to compete on prices.
- the switch cost between standardized products is high.
A country whose currency has a reserve status can borrow at little cost because
- it can repay the loan by printing more money.
- other countries are willing to accumulate a fair amount of the reserve currency.
- its currency is as good as gold.
- its currency does not fluctuate in the foreign exchange market.
- Both A and B.
Expected value
- must exceed a sure thing by a big margin for a risk-averse person to take a bet in the face of potential loss.
- is compared to a sure thing to assess individual risk preference
- is easy to compute because accurate odds of gain and loss are readily available.
- is compared to expected loss to assess individual risk preference
Economic inefficiency can be entrenched by some initial allocation of property rights if
- property rights can be freely and costlessly transferred.
- the property rights are held by many small holders.
- the transaction cost in property transfer is very low.
- the property rights are held by only a few holders.
Statistical discrimination
- treats everybody in the same statistical group fairly.
- hurts those who have higher than average risk in the group being discriminated against.
- benefits those who have higher than average risk in the group being favored.
- is unfair to everybody in the same statistical group.
P = MR under perfect price discrimination because
- each unit is sold at a different highest possible price that could be afforded by the marginal buyer.
- each unit is sold at the same uniform price.
- marginal revenue is by definition equal to price regardless of pricing strategy.
- selling one more unit always brings in revenue equal to the price regardless of pricing strategy.
Scalpers perform a useful function because
- they are primarily concerned that concert promoters would get hurt.
- they recycle their profits to concert promoters.
- they help those who value their tickets more than their money.
- they help to reallocate tickets to those who can most afford to pay.
A disruptive technology usually
- appeals to the high-end users of the current technology from the get go.
- appeals to the low-end users of the current technology because of the technical sophistication it brings.
- comes when there is no dominant technology in the market.
- is ignored by the dominant player in the current technology because of its initial low-profit margin.
Human behavior is predictable because
- Agents continuously optimize their choices at the margin.
- Agents follow behavioral rules that restrict their choice flexibility to deal with uncertainty.
- Human agents are rational.
- Human agents are irrational.
Joint liability
- is less time consuming than objective credit history in expanding the loan circle.
- allows lenders to lend to fewer people.
- reduces the risk of loan default in the absence of objective credit history.
- is more useful as a loan collateral in mobile societies.
A Public Television program on a DVD is sold as a ______ good;
when it is broadcast on the air it is a _______ good; and when it is
re-broadcast on cable television it is a _____ good.
- private; low-congestion; public
- low-congestion; public; private
- private; public; low-congestion
- public; private; low-congestion
Health care insurance is expensive because
- there are more inexpensive medical cures available.
- medical treatment could be easily denied.
- of moral hazard on the part of the insured.
- patients prefer non-treatment to futile treatment.
What does "gross" mean in "gross domestic product"?
- Capital depreciation has been netted out of total output (GDP).
- There is some double counting in the total output (GDP) because some part of the capital investment actually is depreciated for the production of other final goods.
- Capital investment can last over time but consumption vanishes when consumed.
- Not all long-lasting intangible assets have been included.