Prisons essentially
- increase the opportunity cost of prisoners by increasing their opportunity set.
- create a pool of labor who could be employed at below market wages, if the law permits their gainful employment.
- leave the opportunity cost of prisoners the same as when they were free.
- punish the prisoners at little opportunity costs to taxpayers.
Sweat shops exist in America
- where big business is conducted.
- where legal immigrants are employed.
- where illegal immigrants are employed.
- where illegal business is conducted.
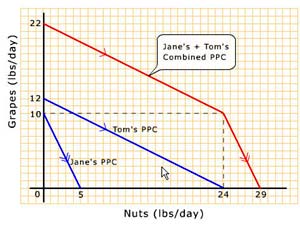
Which points on the combined PPC (PPF) show that Tom and Jane are both producing the same single product?
- The kink of the combined PPC (PPF).
- The vertical and horizontal intercepts.
- Mid-points at each linear segment of the combined PPC (PPF).
- Both A and C.

For any output combination of grapes and nuts attainable
inside the PPC (or PPF), there is at least one corresponding point on
the combined PPC that is superior because
- Tom and Jane each works harder when at least one of them specialize.
- a higher total output combination of grapes and nuts is always better regardless of how the higher output is distributed between Tom and Jane.
- the corresponding point reflects more accurately the consumption bundle that both Tom and Jane prefer.
- the corresponding point has more of at least one good.
Suppose you have 2 hours to watch one of 4 possible movies.
You rank the movies in descending order of their desirability as
follows: (1) Borat; (2) Stomp the Yard; (3) Rocky Balboa; and (4) The
Pursuit of Happyness. The opportunity cost of watching Borat is
- not watching Stomp the Yard.
- not watching The Pursuit of Happyness.
- not watching the other three movies.
- not watching Rocky Balboa.

In terms of the relationship between comparative advantage and
opportunity cost in a two-workers and two-goods economy with two
differently-sloping straight-lined downward-sloping PPCs (or PPFs),
which of the following is true?
- When Tom's opportunity cost of nuts in terms of grapes forgone is lower than Jane's, Tom has a comparative advantage in producing nuts.
- When Tom's opportunity cost of nuts in terms of grapes forgone is lower than Jane's, Tom has a comparative advantage in producing grapes.
- When Jane's opportunity cost of grapes in terms of nuts forgone is lower than Tom's, Tom has a comparative advantage in producing grapes.
- When Tom's opportunity cost of nuts in terms of grapes forgone is lower than Jane's, Jane has a comparative advantage in producing nuts.
Even when the money cost of an activity stays the same, the opportunity cost varies because
- your opportunity set always shrinks.
- your opportunity set stays the same over time.
- your opportunity set always expands.
- your opportunity set changes from time to time.
Opportunity cost includes
- Only out-of-pocket cash cost.
- Out-of-pocket cash cost and highest foregone benefit from non-cash resources.
- Out-of-pocket cash cost and lowest foregone benefit from non-cash resources.
- Highest foregone benefit from non-cash resources only.
Why might some people choose to pay more (buying tickets) to fly than to take a bus for long-distance travel?
- Bus fare actually costs more for those whose time cost is higher.
- Bus fare costs less only for those whose time costs is lower.
- Both A and B.
- Long-distance buses do not have restrooms.
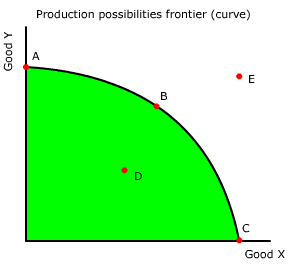
Which of the output combinations on the PPF (PPC) indicates infeasible use of resources?
- D only
- E only
- B only
- A and C only
- A, B and C

Tom's PPC (or PPF) moves upward and Jane's PPC moves rightward to form the combined PPC because
- Starting from maximum joint nut output, Tom is happy with producing and consuming all nuts.
- Starting from maximum joint nut output, it makes sense to first ask Jane who has a lower opportunity cost in producing grapes to give up nuts before asking Tom who has a higher opportunity cost of producing nuts.
- Starting from maximum joint nut output, it makes sense to first ask Tom who has a higher opportunity cost in producing nuts to give up nuts before asking Jane who has a higher opportunity cost of producing nuts.
- Starting from maximum joint nut output, it makes sense to first ask Jane who has a lower opportunity cost in producing grapes to give up nuts before asking Tom who has a higher opportunity cost of producing grapes.
Processed foods (such as canned goods and frozen meals) are more popular today because
- they take shorter time to prepare.
- they allow users to easily customize (lower or increase) the amount of ingredients.
- fewer people know how to cook from scratch any more.
- are healthier because they usually contain the nutritionally recommended amount of salt and trans fat.
- Both A and C.
Which of the following jobs are less likely to be offshored?
- Book-keepers
- Barbers.
- Tax preparers
- Computer programmers.

Which of the output combinations on the PPF (PPC) indicates efficient use of resources?
- E only
- A and C only
- D only
- A, B and C
- B only
Many Americans go or return to college during jobless economic recovery because
- tuition goes down during economic recessions.
- they can get more financial support from their unemployed relatives.
- the government offers more financial help.
- the opportunity cost of college education is lower.
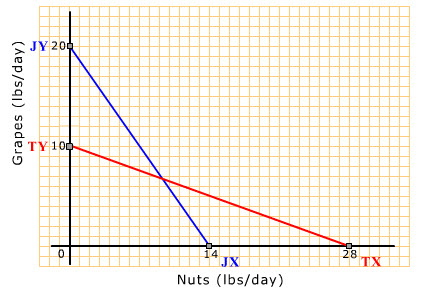
A straight-lined downward sloping production possibility curve (or frontier) in a two-goods economy means that
- the trade-off ratio between one good and the other good is decreasing.
- the trade-off ratio between one good and the other good is constant.
- the trade-off ratio between one good and the other good is increasing.
- the output of both goods can be increased at the same time.
The family wage-gap between women without children and women with children might have
- encouraged career women to have children at a younger age.
- led to a higher concentration of children born to more-educated women with higher opportunity costs.
- led to a higher concentration of children born to less-educated women with higher opportunity costs.
- discouraged highly educated women from having any (or as many) children as they otherwise would.

Which of the following is true along the combined PPC (PPF)?
- Tom and Jane each completely specializes at every point on the curve.
- Tom and Jane each completely specializes only at the vertical or the horizontal intercept.
- Tom and Jane each completely specializes only at the kink of the combined curve.
- All of the above.
- None of the points on the curve shows complete specialization.
Many poor foreigners want to come to the US because
- they are willing to work for less than what they were paid back home.
- the cost of living is higher in the US.
- they get paid more for doing the same jobs in the US than back home.
- they are legally exempt from income tax.
Hiring picketers with lower opportunity costs
- violates the logic of comparative advantage because the hired hands may not believe in the cause.
- puts the same amount of pressure on the employers as a job action.
- makes sense if the picket is intended to only publicize a grievance.
- is an adequate substitute if devotion to the promoted cause on the part of the picketers is required.